Data with nested dictionaries#
Let’s consider the table below, representing a gradebook for a course.
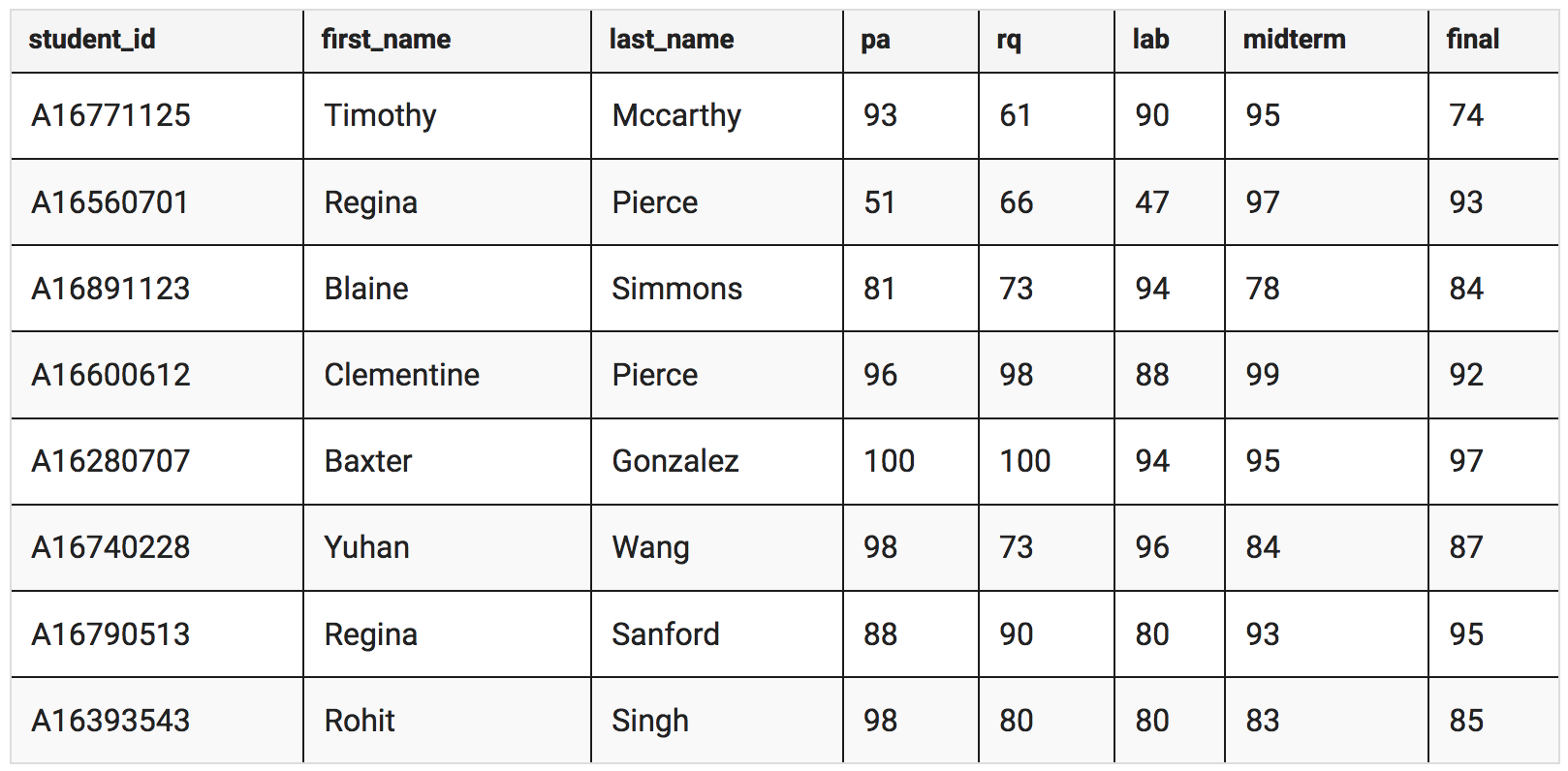
The above table contains information about 8 students such as the student ID, first name, last name of the student followed by the student’s grades for the programming assignment, reading quiz, lab, midterm exam, and final exam for the course.
Now, let’s think of how we can represent this data as a dictionary of dictionaries. Recall that a dictionary consists of a collection of key-value pairs. And that every key in a dictionary should be unique.
If we want to create a dictionary from the above table, first we need to look for a column with unique values so that we can use that as the key for our outer dictionary. And the value for that unique key can be a dictionary (we’ll call it an inner dictionary) again.
So for the above table, the best column to use as a key for the outer dictionary would be the student_id column since each entry in the column is unique which satisfies the condition required for a dictionary key. We can then create an inner dictionary of key-value pairs as the value for the outer dictionary as follows:
student_data = {
'A16771125': {'first_name': 'Timothy', 'last_name': 'Mccarthy', 'pa': 93, 'rq': 61, 'lab': 90,
'midterm': 95, 'final': 74},
'A16560701': {'first_name': 'Regina', 'last_name': 'Pierce', 'pa': 51, 'rq': 66, 'lab': 47,
'midterm': 97, 'final': 93},
'A16891123': {'first_name': 'Blaine', 'last_name': 'Simmons', 'pa': 81, 'rq': 73, 'lab': 94,
'midterm': 78, 'final': 84},
'A16600612': {'first_name': 'Clementine', 'last_name': 'Pierce', 'pa': 96, 'rq': 98, 'lab': 88,
'midterm': 99, 'final': 92},
'A16280707': {'first_name': 'Baxter', 'last_name': 'Gonzalez', 'pa': 100, 'rq': 100, 'lab': 94,
'midterm': 95, 'final': 97},
'A16740228': {'first_name': 'Yuhan', 'last_name': 'Wang', 'pa': 98, 'rq': 73, 'lab': 96,
'midterm': 84, 'final': 87},
'A16790513': {'first_name': 'Regina', 'last_name': 'Sanford', 'pa': 88, 'rq': 90, 'lab': 80,
'midterm': 93, 'final': 95},
'A16393543': {'first_name': 'Rohit', 'last_name': 'Singh', 'pa': 98, 'rq': 80, 'lab': 80,
'midterm': 83, 'final': 85},
}
Here, 'A16771125' is the one of the unique keys of the student_data dictionary and its corresponding value is {'first_name': 'Timothy', 'last_name': 'Mccarthy', 'pa': 93, 'rq': 61, 'lab': 90, 'midterm': 95, 'final': 74} which is a dictionary containing multiple key-value pairs that represent the student’s details and grades for the corresponding student_id which is used as the key.